Multivariate anomaly detection
Multivariate anomaly takes a holistic approach to anomaly detection. It uses all the variables in the training dataset to train the model. This is different from univariate anomaly detection, which uses only one variable and doesn't require a pre-trained model.
To use multivariate anomaly detection, you must training a model using multivariate data. You can use the data generator to generate multivariate data or you can also use your own data.
Multivariate anomaly detection inference is similar to univariate anomaly detection inference. You can use the anomaly detection API to detect anomalies in your data. Data can be sent to the anomaly detection API in one of two ways:
- Batch inference - You can send a batch of data to the anomaly detection API and it will return the predicted anomalies for the data.
- Streaming inference - You can send data to the anomaly detection API one data point at a time. The anomaly detection API will return the predicted anomaly for the data point.
You can find out more Azure Anomaly Detection from the Azure Anomaly Detector documentation.
Create training dataset
You need to create a training dataset that contains the multivariate data that you want to use to train the model. The training dataset consists of the following columns:
timestamp- The timestamp of the data point.- temperature - The temperature of the data point.
- humidity - The humidity of the data point.
- predicted - The predicted anomaly of the data point.
You need around 15000 data points to train the model. Given it's unlikely that you have that much data in your database, you can use a data generator to synthetically generate the data.
Generate the training dataset
In the Notebooks/DemoMultivariateTraining folder there is a Python generator that you can use to generate the training data. The generator will generate a CSV file that you can use to train the model. To run the generator, follow these steps:
From a command line, navigate to the Notebooks/DemoMultivariateTraining folder.
Run the following command.
python3 generator.py
This will generate a CSV file in the Notebooks/DemoMultivariateTraining/training folder. The CSV file will be named sensors.csv.
Train an Anomaly Detection multivariate model
Navigate to the Notebooks folder.
Start the Jupyter Notebook server by running the following command:
jupyter notebookOpen the DemoMultivariateTraining/multivariate_train_from_timeseries_data.ipynb notebook. Note, the Notebook defaults to analyzing 7 days data for device hvac_simulator
Run all the cells in the notebook.
You'll notice the Train a model cell will take a while to run. This is because it's training the model using the data that you generated in the previous step. The training process will take a few minutes to complete. When the training process is complete. The output for this cell will be similar to the following:
model id: 9990b402-8041-11ed-b12c-f2dc2fbc265b
model status: CREATED
model status: RUNNING
model status: READYMake a note of the model id as you must update the Notebooks/.env file with this model id.
Detect anomalies using the multivariate model
Navigate to the
Notebooksfolder.Start the Jupyter Notebook server by running the following command:
jupyter notebookA browser window will open and display the Jupyter Notebook dashboard. Click on the
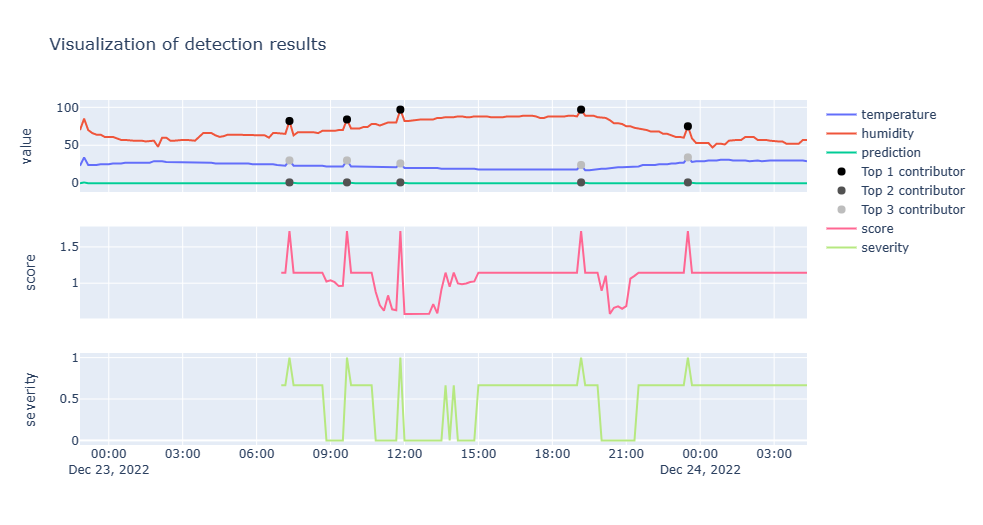
multivariate_sql_inference_plot.ipynbnotebook to open it.Run the notebook cells one at a time. The notebook will walk you through the process of loading the data, training the model, and detecting anomalies.
The notebook will show a plot of the predicted anomalies.